What Is a Good Tds Reading for Ro Water
TDS AND pH FACT Canvass
What are TDS?
TDS stands for total dissolved solids, and represents the full concentration of dissolved substances in water. TDS is made upwards of inorganic salts, every bit well as a small-scale amount of organic thing. Mutual inorganic salts that can exist plant in water include calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium, which are all cations, and carbonates, nitrates, bicarbonates, chlorides and sulfates, which are all anions. Cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged ions.
How do These Solids End Up Dissolved in Water?
These minerals can originate from a number of sources, both natural and as a result of human activities. Mineral springs contain water with high levels of dissolved solids, because the h2o has flowed through a region where the rocks have a high salt content. The water in the Prairie provinces tends to accept high levels of dissolved solids, considering of high amounts of calcium and magnesium in the footing.
These minerals can besides come from human activities. Agricultural and urban runoff tin conduct excess minerals into water sources, as can wastewater discharges, industrial wastewater and salt that is used to de-ice roads.
What Happens to the Water When the TDS Level is High?
Lone, a high concentration of dissolved solids is unremarkably not a health hazard. In fact, many people buy mineral water, which has naturally elevated levels of dissolved solids. The U.s. Ecology Protection Agency (EPA), which is responsible for drinking h2o regulations in the U.s.a., includes TDS as a secondary standard, meaning that it is a voluntary guideline in the United States. While the United States set legal standards for many harmful substances, TDS, forth with other contaminants that cause aesthetic, cosmetic and technical effects, has only a guideline.
Most people call back of TDS every bit being an artful gene. In a report by the World Wellness Organization, a console of tasters came to the following conclusions nigh the preferable level of TDS in water:
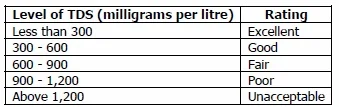
Taste of Water with Different TDS Concentrations;
http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/tds.pdf
Withal, a very depression concentration of TDS has been found to requite water a flat taste, which is undesirable to many people.
Increased concentrations of dissolved solids can as well accept technical furnishings. Dissolved solids can produce hard water, which leaves deposits and films on fixtures, and on the insides of hot water pipes and boilers. Soaps and detergents practice not produce as much lather with hard h2o equally with soft h2o. As well, high amounts of dissolved solids can stain household fixtures, corrode pipes, and have a metallic taste. Difficult water causes water filters to wear out sooner, because of the amount of minerals in the water. The picture below was taken near the Mammoth Hot Springs, in Yellowstone National Park, and shows the consequence that h2o with high concentrations of minerals tin can accept on the mural. The same minerals that are deposited on these rocks tin can cause issues when they build up in pipes and fixtures.
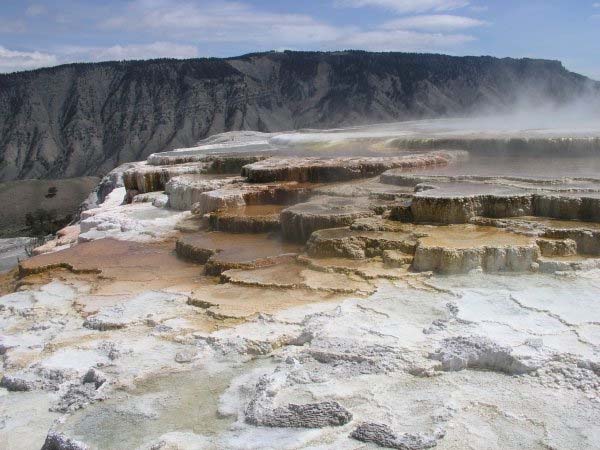

Mineral Degradation from Minerals in Water at Mammoth Hot Springs
However, while TDS itself may be only an aesthetic and technical gene, a loftier concentration of TDS is an indicator that harmful contaminants, such as atomic number 26, manganese, sulfate, bromide and arsenic, tin can also be present in the water. This is especially true when the excessive dissolved solids are added to the water as human pollution, through runoff and wastewater discharges.
What are the Guidelines for TDS?
In Canada, substances that are considered to exist dangerous in high amounts are listed equally Maximum Acceptable Concentrations (MACs) in the Canadian Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality. Nonetheless, substances that are non considered dangerous at their MAC, such equally TDS, are given an aesthetic objective in the Guidelines. The Canadian guideline for TDS is less than 500 milligrams per litre (which is the same as 500 parts per million). However, since the Canadian guidelines are not enforceable, each province is gratuitous to choose whether or not they will follow the guidelines. Saskatchewan has water that naturally contains high concentrations of TDS, so the province has chosen to not follow the Canadian guideline of 500 parts per million, and to implement its own guideline of 1,500 parts per one thousand thousand.
In the United States, substances that are health-based accept Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs), and are enforceable by constabulary. All the same, TDS, and other substances that are considered artful, are given Secondary Maximum Contaminant Levels (SMCLs), but are not enforced, because they do not pose as great a health risk as the primary contaminants do. The Usa guideline for TDS is also 500 parts per million.
How Can Water Treatment Facilities Remove TDS?
H2o treatment facilities can use reverse osmosis to remove the dissolved solids in the h2o that are responsible for elevated TDS levels. Opposite osmosis removes virtually all dissolved substances, including many harmful minerals, such as salt and pb. It besides removes healthy minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, and ideally such water should be filtered through a magnesium and calcium mineral bed to add the minerals to the h2o. The mineral bed also increases the pH and decreases the corrosive potential of the water. For more information about reverse osmosis, meet the Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis fact canvas.
What is pH?
The pH value of a h2o source is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. The pH level is a measurement of the activity of the hydrogen cantlet, because the hydrogen activity is a good representation of the acerbity or alkalinity of the water. The pH scale, equally shown below, ranges from 0 to 14, with seven.0 existence neutral. Water with a depression pH is said to be acidic, and water with a loftier pH is bones, or element of group i. Pure h2o would accept a pH of 7.0, just water sources and precipitation tends to exist slightly acidic, due to contaminants that are in the water.
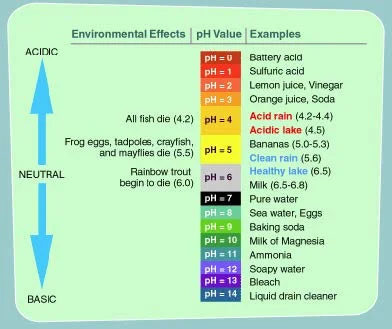
pH Scale
The pH scale is logarithmic, which means that each step on the pH scale represents a ten-fold change in acidity. For case, a water torso with a pH of five.0 is ten times more acidic than water with a pH of six.0. And water with a pH of four.0 is 100 times more than acidic than h2o with a pH of six.0.
How Does the pH of a Water Source Alter?
Surface water typically has a pH value between 6.five and 8.five and groundwater tends to have a pH betwixt 6.0 and 8.5. The pH of a water source can vary naturally. Some types of rock and soil, such equally limestone, can neutralize acid more effectively than other types of stone and soil, such as granite. Or, when there are a big number of plants growing in a lake or river, they release carbon dioxide when they dice and decompose. When the carbon dioxide mixes with the water, a weak carbonic acrid is formed; this can and so cause the pH of the water body to decrease.
A number of human activities accept a harmful effect on the pH of nearby water sources. When sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are emitted, through industrial operations and vehicles, acid rain tin be produced. For more information about acid rain, see the Acid Rain fact sheet.
Chemical pollution, from industrial operations, individuals and communities, can cause a water body to become acidic. These chemicals can enter the water through illegal discharges or after inadequate wastewater treatment. For more than information about chemical pollution, including ways in which you tin minimize pollution, see the Water Pollution fact canvas.
What Happens When the pH of the Water Changes?
A change in the pH of water tin accept a number of consequences. In the environment, many plants and animals are harmed, or fifty-fifty killed, as a result of acidification. Many varieties of fish and aquatic life are extremely sensitive to changes in water temperature and composition. The below diagram illustrates the pH that is required for a number of aquatic species. Notice that when the pH is effectually half dozen.0 to 7.0 (which is natural for many lakes and streams), the biodiversity within the ecosystem is wide. Equally the pH decreases and the acidity increases, fewer and fewer organisms can survive.
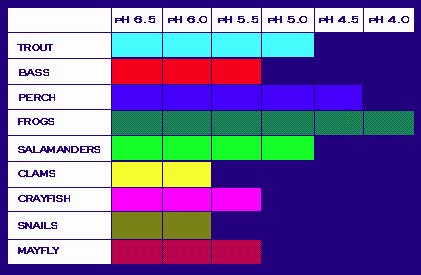
Required pH Level for the Survival of Common Species of Fish
Acidic h2o is synergistic, which means that a combination of a depression pH and an increased concentration of certain substances is far more than harmful than the sum of the parts. For example, aluminium, lead and mercury are potentially dangerous substances, just when the pH of the water source is already low, these substances can accept extremely detrimental consequences for aquatic life.
Acidic h2o can also crusade issues for human consumption. While slightly acidic water is non dangerous, on its own, information technology can be quite dangerous when combined with other compounds. Water with a pH that is less than 6.5 can leach metal ions, including fe, manganese, copper, pb and zinc from plumbing fixtures and pipes. This, in render, can exist quite dangerous. On the other terminate of the pH scale, water that has a pH greater than 8.0 can exist difficult to disinfect. The World Health Organization recommends that the pH of the h2o exist less than viii.0, because basic water does not let for constructive chlorination.
What are the Guidelines for pH?
Like TDS, pH is given an aesthetic objective in Canada. The Canadian Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality suggest that the pH of drinking water should exist betwixt 7.0 and ten.5. The Saskatchewan Drinking Water Standards and Objectives recommend that the pH of drinking water exist between 6.five and 9.0.
In the Usa, pH is, like TDS, a secondary standard; the Secondary Maximum Contaminant Level for pH is betwixt 6.v and viii.5. Co-ordinate to the EPA, the noticeable effects of a pH that is less than half-dozen.5 include a bitter, metallic taste and corrosion. The noticeable effects of a pH above 8.5 include a slippery feeling, soda-like taste and deposits.
How do H2o Treatment Facilities Change the pH of Water?
There are several methods that tin increase the pH of water, before disinfection. The pH is commonly increased using sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide, only a ameliorate fashion of dealing with low pH is to use calcium and magnesium carbonate, which not only volition increment pH levels, but will also make the h2o less corrosive and both calcium and magnesium are of health benefits as opposed to sodium.
Why is it Of import to Monitor TDS and pH?
It is important to monitor the TDS level and the pH of drinking h2o for several reasons. When a water source has a high level of TDS or a low pH, it is likely that there are other harmful contaminants in the water. Both TDS and pH are also piece of cake to measure and if something is happening to a h2o, such as pollution, chances are both TDS and pH levels will change so keeping track of those changes tin act as an early warning signal that something is happening to the water. For these reasons, it is of import to monitor the TDS and pH levels, so that if they change, action can be taken immediately.
For more than information about TDS and pH, including the ways in which you lot can employ these tests on your drinking h2o, see the Operation Water Pollution programme.
The Safe Drinking H2o Foundation has educational programs that can supplement the data institute in this fact canvass. Operation H2o Drop looks at the chemical contaminants that are found in water; information technology is designed for a science class. Functioning H2o Menstruation looks at how water is used, where it comes from and how much it costs; it has lessons that are designed for Social Studies, Math, Biological science, Chemistry and Science classes. Operation H2o Spirit presents a Start Nations perspective of water and the surrounding issues; information technology is designed for Native Studies or Social Studies classes. Operation H2o Health looks at mutual health issues surrounding drinking h2o in Canada and around the world and is designed for a Health, Scientific discipline and Social Studies collaboration. Performance Water Pollution focuses on how water pollution occurs and how it is cleaned up and has been designed for a Science and Social Studies collaboration. To admission more data on these and other educational activities, as well as additional fact sheets, visit the Safety Drinking Water Foundation website at www.safewater.org.
Did you lot detect this information useful? Please assist the states to send digital TDS and digital pH meters which are guaranteed to work for at to the lowest degree ii years to schools! Please chip in $5 or donate $xx or more than and receive an Official Donation Receipt for Income Taxation Purposes - or donate $170 to provide an Operation Water Pollution kit for a school.
Source: https://www.safewater.org/fact-sheets-1/2017/1/23/tds-and-ph
0 Response to "What Is a Good Tds Reading for Ro Water"
Post a Comment